
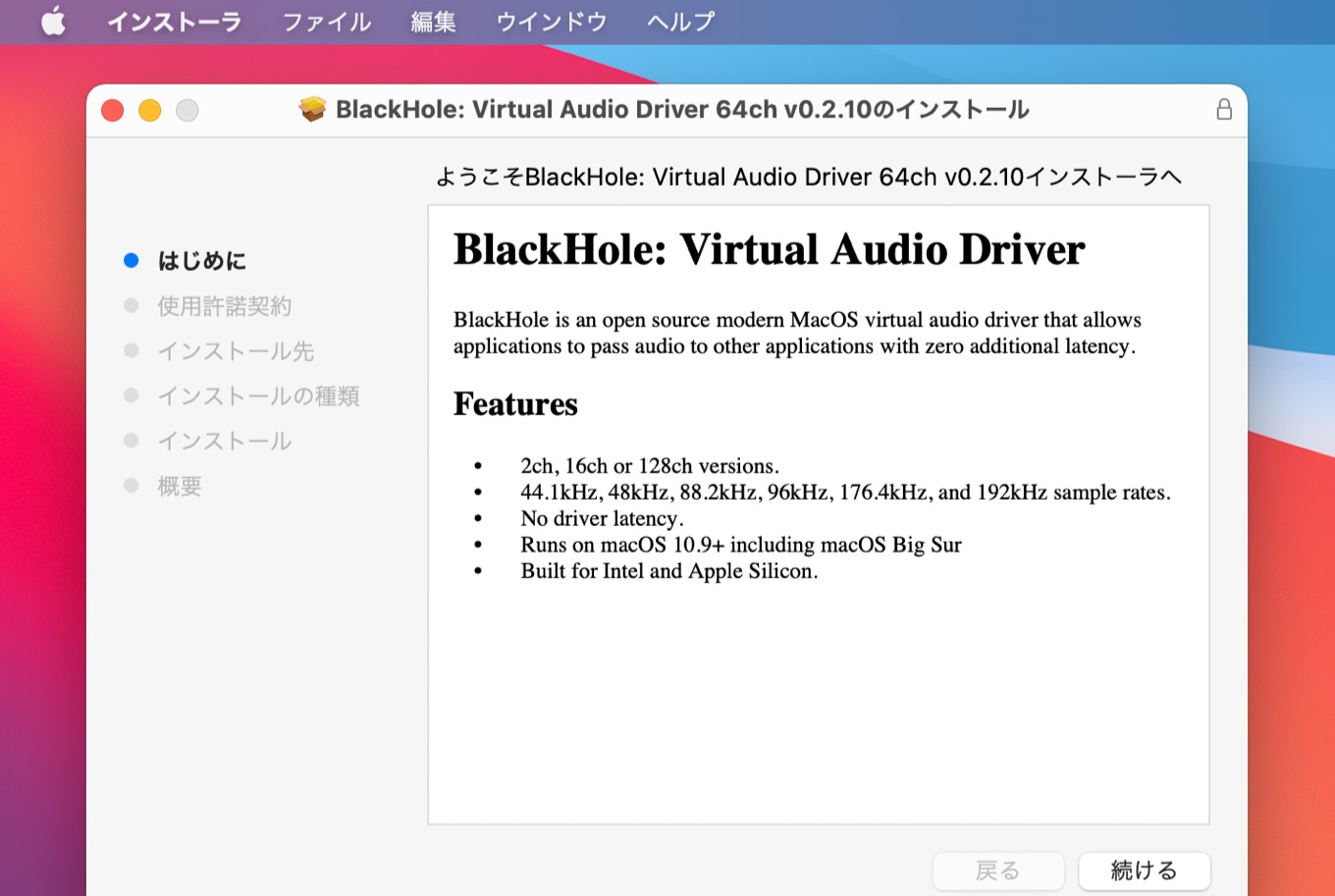
DNSBLs are most often used to publish the addresses of computers or networks linked to spamming most mail server software can be configured to reject or flag messages which have been sent from a site listed on one or more such lists. Main article: Domain Name System-based Blackhole ListĪ DNS-based Blackhole List ( DNSBL) or Real-time Blackhole List ( RBL) is a list of IP addresses published through the Internet Domain Name System (DNS) either as a zone file that can be used by DNS server software, or as a live DNS zone that can be queried in real-time. Typically, classification is limited to the destination IP address prefix, source IP address and incoming network interface. It is bound to be stateless due to the nature of IP routers. Routing typically only works on the Internet Protocol layer and is very limited in packet classification. Blackhole filtering can also be abused by malicious attackers on compromised routers to filter out traffic destined to a certain address.

For this reason, null routes are often used on high-performance core routers to mitigate large-scale denial-of-service attacks before the packets reach a bottleneck, thus avoiding collateral damage from DDoS attacks - although the target of the attack will be inaccessible to anyone. Due to the nature of high-bandwidth routers, null routing can often sustain higher throughput than conventional firewalls. Null routing has an advantage over classic firewalls since it is available on every potential network router (including all modern operating systems), and adds virtually no performance impact. Null routes are typically configured with a special route flag, but can also be implemented by forwarding packets to an illegal IP address such as 0.0.0.0, or the loopback address. The Internet Exchange (IX) provider usually acquires this technology to help its members or participants to filter such attack Remote Triggered Black Hole Filtering (RTBH) is a technique that provides the ability to drop undesirable traffic before it enters a protected network. The rest of this article deals with null routing in the Internet Protocol (IP).īlack hole filtering refers specifically to dropping packets at the routing level, usually using a routing protocol to implement the filtering on several routers at once, often dynamically to respond quickly to distributed denial-of-service attacks. The act of using null routes is often called blackhole filtering. Matching packets are dropped (ignored) rather than forwarded, acting as a kind of very limited firewall. Black hole filtering Ī null route or black hole route is a network route ( routing table entry) that goes nowhere. Network address translation (NAT), as used in home and office routers, is generally a more effective way of obscuring the layout of an internal network. Personal firewalls that do not respond to ICMP echo requests ("ping") have been designated by some vendors as being in "stealth mode".ĭespite this, in most networks the IP addresses of hosts with firewalls configured in this way are easily distinguished from invalid or otherwise unreachable IP addresses: On encountering the latter, a router will generally respond with an ICMP network rsp. Most firewalls (and routers for household use) can be configured to silently discard packets addressed to forbidden hosts or ports, resulting in small or large "black holes" in the network.
For example, 198.51.100.0 / 24 is reserved for use in documentation and examples by RFC 5737 while the RFC advises that the addresses in this range are not routed, this is not a requirement. Connection-oriented or reliable protocols (TCP, RUDP) will either fail to connect to a dead address or will fail to receive expected acknowledgements.įor IPv6, the black hole prefix 100:: / 64 is described by RFC 6666.įor IPv4, no black hole address is explicitly defined, however the reserved IP addresses can help achieve a similar effect. Note that a dead address will be undetectable only to protocols that are both connectionless and unreliable (e.g., UDP). The most common form of black hole is simply an IP address that specifies a host machine that is not running or an address to which no host has been assigned.Įven though TCP/IP provides a means of communicating the delivery failure back to the sender via ICMP, traffic destined for such addresses is often just dropped. When examining the topology of the network, the black holes themselves are invisible, and can only be detected by monitoring the lost traffic hence the name as astronomical black holes cannot be directly observed. In networking, a black hole, also known as a block hole, refers to a place in the network where incoming or outgoing traffic is silently discarded (or "dropped"), without informing the source that the data did not reach its intended recipient.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
