

To minimize the amount of time needed, Processor 2 should do the 80-second step, and Processor 1 should do the 40 and 50-second steps sequentially. Let's call the two Processors Processor 1 and Processor 2. Generally, you'll be looking for the minimum possible time, so we're going to want to do the longer processes first and at the same time.
SEQUENTIAL PROGRAM FASTER THAN PARALLEL FREE
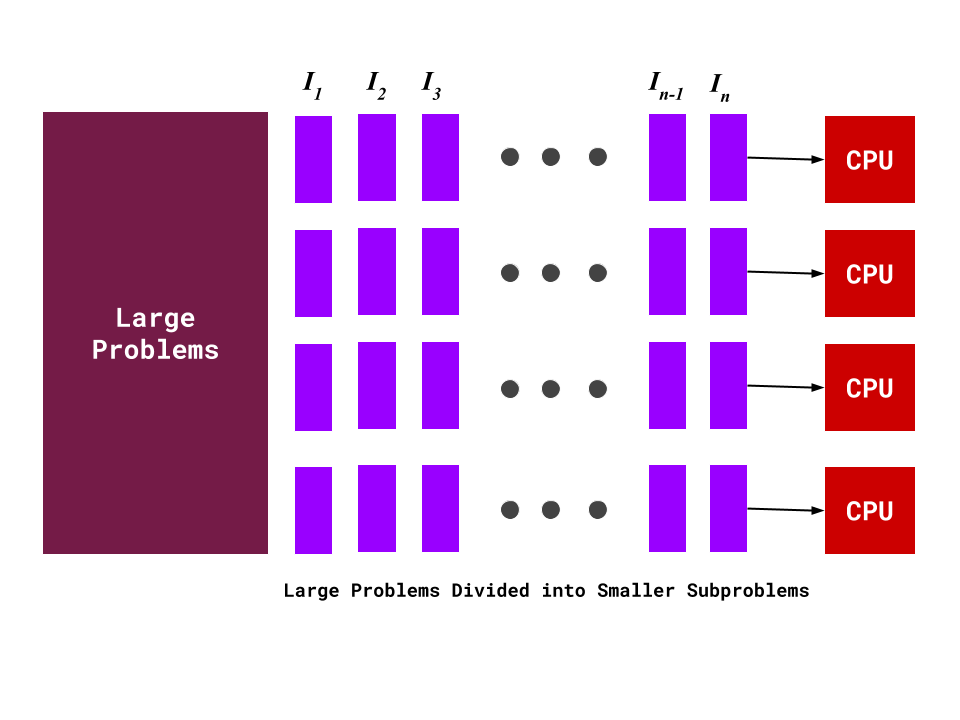
Therefore, the processors are free to do the steps in any order or combination. The 40-second step, for example, doesn't depend on the result of the 80-second step in order to start. Well, it's important to first acknowledge that we're working under the assumption that all steps are independent. Going back to our original example with those three steps of 40, 50, and 80 seconds, a parallel computing solution where two processors are running would take 90 seconds to complete at its fastest. One of the best ways to understand this calculation is with examples. The more cores, the faster (to an extent) the solution is. The speed of a parallel computing solution, on the other hand, depends on the number of cores involved. For example, if your program has three steps that take 40, 50, and 80 seconds respectively, the sequential solution would take 170 seconds to complete. Calculating Execution Time Sequential SolutionsĪ sequential solution takes as long as the sum of all steps in the program. Finally, the test may ask you to calculate the speedup of a certain parallel solution. They may also ask you to compare the efficiency of two solutions. The test may ask you to calculate the execution time of a sequential or a parallel computing solution. The AP CSP test will have conceptual questions about parallel and distributed computing, but they'll also have some calculation questions, too. Execution Time, Efficiency, and Speedup Calculations They come with the added perk of not melting your computer while they're doing it. Modern search engines, applications that store data somewhere separate from the user's computer like Gmail and Google Docs, and *sigh* cryptocurrency mining all use distributed computing.ĭue to their increased capacities, a parallel or distributed computing model can process large data sets or solve complex problems faster than a sequential computing model can. Using distributed computing allows people to solve problems that they wouldn't be able to otherwise, due to a lack of storage or needing too much processing time otherwise. You get the power of two (or more) computers working on the same problem. With a distributed computing model, two "heads" are better than one. These devices can be in different locations around the world, communicating by sending messages to each other. This means if there's a change in scale (ex: more instructions to process than before), these solutions will handle the change better than sequential computing models would.ĭistributed computing, on the other hand, is where multiple devices are used to run a program. Parallel computing solutions are also able to scale more effectively than sequential solutions. Performing tasks at the same time helps to save a lot of time, and money as well. There are several advantages to parallel computing. Most modern computers use parallel computing systems, with anywhere from 4 to 24 cores (or processors) running at the same time. Some of these operations are done at the same time using multiple processors. Parallel computing is where a program is broken into smaller sequential computing operations. Parallel and Distributed Computing Definitions This problem led to the creation of new models of computing known as parallel and distributed computing. A very accurate representation of the melting process Image source: cicoGIFs


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
